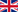
Malachite
Formulal: Cu2[(OH)2|CO3] Hardness: 3,5 - 4
Malachite is a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral. This opaque, green-banded mineral crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, and most often forms botryoidal, fibrous, or stalagmitic masses, in fractures and deep, underground spaces, where the water table and hydrothermal fluids provide the means for chemical precipitation. Individual crystals are rare, but occur as slender to acicular prisms. Pseudomorphs after more tabular or blocky azurite crystals also occur.
The stone's name derives (via Latin: molochītis, Middle French: melochite, and Middle English melochites) from Greek Μολοχίτης λίθος molochites lithos, "mallow-green stone", from μολόχη molochē, variant of μαλάχη malāchē, "mallow". The mineral was given this name due to its resemblance to the leaves of the mallow plant. Malachite was extensively mined at the Great Orme Mines in Britain 3,800 years ago, using stone and bone tools. Archaeological evidence indicates that mining activity ended c. 600 BCE, with up to 1,760 tonnes of copper being produced from the mined Malachite. Archaeological evidence indicates that the mineral has been mined and smelted to obtain copper at Timna Valley in Israel for more than 3,000 years. Since then, malachite has been used as both an ornamental stone and as a gemstone.
JoomShopping Download & Support